

What is gum disease?
Gum disease refers to inflammation of the soft tissue (gingiva) and abnormal loss of bone that surrounds the teeth and holds them in place. Gum disease is the second most common cause of toothache.
What causes gum disease?
Gum disease is caused by toxins secreted by bacteria in "plaque" that accumulate over time along the gum line.This plaque is a mixture of food, saliva, and bacteria.
What are symptoms of gum disease?
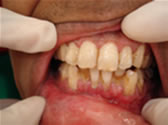
Early symptoms of gum disease include gum bleeding without pain. Pain is a symptom of more advanced gum disease as the loss of bone around the teeth leads to the formation of gum pockets. Bacteria in these pockets cause gum infection, swelling, pain, and further bone destruction. Advanced gum disease can cause loss of otherwise healthy teeth.
How is gum disease treated?
Treatment of early gum disease involves oral hygiene and removal of bacterial plaque. Moderate to advanced gum disease usually requires a thorough cleaning of the teeth and teeth roots called "root planing" and "subgingival curettage." Root planing is the removal of plaque and tartar (hardened plaque) from exposed teeth roots while subgingival curettage refers to the removal of the surface of the inflamed layer of gum tissue. Both of these procedures are usually performed under local anesthesia and may be accompanied by the use of oral antibiotics to overcome gum infection or abscess. Follow-up treatment may include various types of gum surgeries. In advanced gum disease with significant bone destruction and loosening of teeth, teeth splinting or teeth extractions may be necessary.
Periodontitis
It is a progressive inflammatory disease of the gums and the surrounding tissue around the teeth. It is commonly known as gum disease and was referred to as pyorrhea in the old days. It is estimated that up to 80% of the population above the age of 40 may suffer from this disease with the severity varying drastically from one person to another. Periodontitis is the number one cause of tooth loss after the age of 40.
Certain medical conditions or medications can make you more susceptible to gum disease. They include pregnancy, diabetes, epilepsy, and such medications as chemotherapy, birth control pills, antidepressants, and those for heart problems.
If you notice any of the following signs of gum disease, schedule an appointment immediately:
 |
 |
When gum is inflamed severely (periodontitis), alveolar bone will be absorbed, and defected. Periodontal ligaments which connect between the alveolar bone and the teeth will disappear. Sever bone lose will cause tooth moving and missing. Flap and bone surgery is order to contour the bone, deeply clean the tooth to reduce the inflammation, and promote bone re-growing and connections firm.
|
|
|
|
|
Fig. 1 |
Fig. 2 |
Fig. 3 |
Fig. 4 |
Fig. 5 |